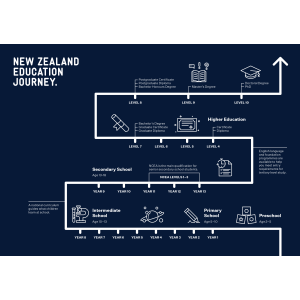
The New Zealand Education System
From early childhood to PhD, the learning journey in New Zealand
What are the different levels of Education in New Zealand?
Early Childhood Education (ECE) in New Zealand
Education in New Zealand starts with Early Childhood Education (ECE). While ECE is not mandatory, a huge majority (almost 97%) of parents enroll their children in some form of pre-school education. The New Zealand government subsidises ECE for all students for up to 20 hours per working week.
You will find the following types of ECE in New Zealand:
- Teacher-led Learning: Enrolling in a pre-school where learning is directed by a trained teacher.
- Kindergartens: Accept children aged 2-5 years and educate them based on a set timetable.
- Education & Care Services: Offer flexible hour programs for children from birth to primary school.
- Home-based Education & Care: Provides education and care services for children from newborn to 5 years old through a certified ECE teacher who reports to their coordinators.
- Te Kura: A correspondence school offering learning programs for children aged 3-5 years who face learning difficulties.
Primary & Secondary Education in New Zealand
Following ECE, the New Zealand's education system leads into primary and secondary education. Education is free for domestic students aged 5-19 attending state or government-funded primary and senior secondary schools. Schooling is compulsory for students aged 6-16. Admissions to primary schools usually begin either at the start of the school year for a group of students or individually when a child turns 5 or 6. Most students attend school until the age of 17. The school education system is divided into 13 years comprising of primary Education for students aged 5-12 years, covering Year 1 to Year 8, and secondary Education for students aged 13-17 years, covering Year 9 to Year 13.
Tertiary Education in New Zealand
After completing secondary education, students can pursue their studies into tertiary education. Tertiary education includes vocational training, undergraduate degrees, and postgraduate degrees, up to PhD level, at various universities, polytechs (IPTs), or private institutes.
It is generally understood that tertiary education starts at level 4, progressing through certificates, diplomas, degrees, and doctorates. The table below indicates the various qualifications listed under each level.
A certificate at level 4 qualifies individuals to work or study in broad or specialised field(s)/ areas.
Outcomes
A graduate of a level 4 certificate is able to:
- demonstrate broad operational and theoretical knowledge in a field of work or study
- select and apply solutions to familiar and sometimes unfamiliar problems
- select and apply a range of standard and non-standard processes relevant to the field of work or study
- apply a range of communication skills relevant to the field of work or study
- demonstrate the self-management of learning and performance under broad guidance
- demonstrate some responsibility for performance of others.
Credits
This certificate is listed at level 4 and must comprise a minimum of 40 credits at level 4 or above.
Certificate level 5
A certificate at level 5 qualifies individuals with theoretical and/or technical knowledge and skills within an aspect(s) of a specific field of work or study.
Outcomes
A graduate of a level 5 certificate is able to: •
- demonstrate broad operational or technical and theoretical knowledge within an aspect(s) of a specific field of work or study
- select and apply a range of solutions to familiar and sometimes unfamiliar problems
- select and apply a range of standard and non-standard processes relevant to the field of work or study
- demonstrate complete self-management of learning and performance within defined contexts
- demonstrate some responsibility for the management of learning and performance of others.
Credit requirements
This certificate is listed at level 5 and must comprise a minimum of 40 credits at level 5 or above.
Diploma level 5
A diploma at level 5 qualifies individuals with theoretical and/or technical knowledge and skills within a specific field of work or study.
Outcomes
A graduate of a level 5 diploma is able to:
- demonstrate broad operational or technical and theoretical knowledge within a specific field of work or study
- select and apply a range of solutions to familiar and sometimes unfamiliar problems
- select and apply a range of standard and non-standard processes relevant to the field of work or study
- demonstrate complete self-management of learning and performance within defined contexts
- demonstrate some responsibility for the management of learning and performance of others.
Credit requirements
This diploma is listed at level 5. It must contain a minimum of 120 credits from level 4 or above including at least 72 credits at level 5 or above.
Certificate level 6
Purpose A certificate at level 6 qualifies individuals with theoretical and/or technical knowledge and skills within an aspect(s) of a specialised/strategic context.
Outcomes
A graduate of a level 6 certificate is able to:
- demonstrate specialised technical or theoretical knowledge with depth within an aspect(s) of a field of work or study
- analyse and generate solutions to familiar and unfamiliar problems
- select and apply a range of standard and non-standard processes relevant to the field of work or study • demonstrate complete self-management of learning and performance within dynamic contexts
- demonstrate responsibility for leadership within dynamic contexts.
Credit requirements
This certificate is listed at level 6 and must comprise a minimum of 40 credits at level 6 or above.
Diploma level 6
A diploma at level 6 qualifies individuals with theoretical and/or technical knowledge and skills in specialised/strategic contexts.
Outcomes
A graduate of a level 6 diploma is able to:
- demonstrate specialised technical or theoretical knowledge with depth in a field of work or study
- analyse and generate solutions to familiar and unfamiliar problems
- select and apply a range of standard and non-standard processes relevant to the field of work or study
- demonstrate complete self-management of learning and performance within dynamic contexts
- demonstrate responsibility for leadership within dynamic contexts.
Credit requirements
This diploma is listed at level 6. It must contain a minimum of 120 credits from level 5 or above including at least 72 credits at level 6 or above
Diploma level 7
A diploma at level 7 qualifies individuals with specialised and technical knowledge and skills within a professional context.
Outcomes
A graduate of a level 7 diploma is able to:
- demonstrate specialised technical or theoretical knowledge with depth in one or more fields of work or study
- analyse and generate solutions to unfamiliar and sometimes complex problems
- select, adapt and apply a range of processes relevant to the field of work or study
- demonstrate advanced generic skills and/or specialist knowledge and skills in a professional context or field of study.
Credit requirements
This diploma is listed at level 7. It must contain a minimum of 120 credits from level 5 or above including at least 72 credits at level 7 or above.
Bachelor’s Degree
A Bachelor’s Degree provides individuals with a systematic and coherent introduction to a body of knowledge of a recognised major subject (or subjects, in the case of a double degree or a double major) as well as to problem-solving and associated basic techniques of self-directed work and learning.
A Bachelor’s Degree involves at least one sequential study programme in which content is progressively developed such that it might form a basis for postgraduate study and/or professional practice. Bachelor’s Degrees are taught mainly by people engaged in research4 (see Section 253B of the Education Act 1989).
Entry
A programme of study leading to a Bachelor’s Degree builds on prior study, work or experience, and is open to those who have met the specified entrance requirements, normally at level 3 on the NZQF.
Outcomes
A graduate of a Bachelor’s Degree is able to:
- demonstrate intellectual independence, critical thinking and analytic rigour
- engage in self-directed learning
- demonstrate knowledge and skills related to the ideas, principles, concepts, chief research methods and problem-solving techniques of a recognised major subject
- demonstrate the skills needed to acquire, understand and assess information from a range of sources
- demonstrate communication and collaborative skills.
Credit requirements
A Bachelor’s Degree requires a minimum of 360 credits from levels 5 to 7. Of the credits required for a Bachelor Degree, a minimum of 72 credits must be at level 7 or higher. The degree should specify a spread of credit across levels, so that the qualification demonstrates progression, reflects the requirements of the degree definition and achieves the associated learning outcomes in a way that is appropriate to the subject area.
Relationship with other qualifications
A person who holds a Bachelor’s Degree might be eligible to enrol in a Postgraduate qualification.
Graduate Certificate
A Graduate Certificate is designed primarily as a vehicle for degree graduates to pursue further study at an advanced undergraduate level. The Graduate Certificate is typically designed as a bridging qualification to postgraduate study for individuals developing educational, professional or vocational knowledge in a new discipline, profession or subject area and/or as a broadening or deepening of skills or knowledge already gained in an undergraduate qualification.
Entry
Entry is open to degree graduates. However, subject to the regulations of the award, those who have been able to demonstrate equivalent practical, professional or educational experience of an appropriate kind may be granted admission.
Outcomes
In addition to the Bachelor Degree outcomes, a person with a Graduate Certificate is able to demonstrate some outcomes of a Bachelor Degree in a new area of study. Credit requirements The Graduate Certificate requires a minimum of 60 credits, with a minimum of 40 at level 7 or above.
Relationship with other qualifications
A Graduate Certificate may provide the basis for postgraduate study.
Graduate Diploma
A Graduate Diploma allows degree graduates to pursue a significant body of study at an advanced undergraduate level. The Diploma is typically designed as a bridging qualification to postgraduate study as well as broadening knowledge and skills in a familiar subject or discipline, or developing knowledge in a new area.
Entry
Entry is open to degree graduates. However, subject to the regulations of the award, those who have been able to demonstrate equivalent practical, professional or educational experience of an appropriate kind may be granted admission.
Outcomes
In addition to the Bachelor Degree outcomes, a person with a Graduate Diploma is able to demonstrate outcomes of a Bachelor Degree in a new area of study.
Credit requirements
A Graduate Diploma requires a minimum of 120 credits, of which 72 credits must be at level 7 or above.
Relationship with other qualifications
A Graduate Diploma may provide the basis for postgraduate study.
Bachelor Honours Degree
A Bachelor Honours Degree recognises distinguished study at level 8. It may either be a degree in itself, or a discrete postgraduate degree following a Bachelor Degree. The award of honours recognises outstanding achievement, meritorious achievement or a pass; these may be termed first class honours, second class honours: first or second divisions, and third class honours.
Entry
Entry to honours study is normally based on achievement of above average performance in the credits within the Bachelor Degree that are relevant to the proposed honours study.
Outcomes
A graduate of a Bachelor Honours Degree is able to:
- engage in self-directed learning and advanced study
- demonstrate intellectual independence, analytic rigour, and the ability to understand and evaluate new knowledge and ideas
- demonstrate the ability to identify topics for original research, plan and conduct research, analyse results, and communicate the findings to the satisfaction of subject experts.
Credit requirements
A Bachelor Honours Degree may be either a 480-credit degree, or a discrete 120-credit degree following a Bachelor Degree. The degree has a minimum of 120 credits at level 8, with a research component that represents at least 30 credits at that level.
Relationship with other qualifications
Achieved to an appropriate standard, a Bachelor Honours Degree should prepare graduates for admission to further postgraduate study
Postgraduate Certificate
The Postgraduate Certificate is designed to extend and deepen an individual’s knowledge and skills. The Postgraduate Certificate involves credits from a specified subject and cognate areas. It recognises continuing professional development or academic achievement in advance of a Bachelor degree in the same area as the individual’s original degree or Graduate Certificate or Diploma.
Entry
Postgraduate Certificates require either a Bachelor Degree or Graduate Certificate or Diploma in a cognate subject, or relevant skills and knowledge acquired through appropriate work or professional experience.
Outcomes
A graduate of a Postgraduate Certificate is able to show evidence of advanced knowledge about a specialist field of enquiry or professional practice. Credit requirements The Postgraduate Certificate requires a minimum of 60 credits at level 8.
Relationship with other qualifications
A Postgraduate Certificate provides the basis for further postgraduate study
Postgraduate Diploma
A Postgraduate Diploma is designed to extend and deepen an individual’s knowledge and skills by building on attainment in the principal subject(s) of the qualifying degree, graduate diploma or graduate certificate. A Postgraduate Diploma prepares an individual for independent research and scholarship in the principal subject of the diploma. A Postgraduate Diploma may be awarded with distinction.
Entry
An individual for the Postgraduate Diploma in a specified subject or, where appropriate, a related area will normally have completed all requirements of the relevant Bachelor Degree or Graduate Certificate or Diploma, or is deemed to have acquired the relevant skills and knowledge through appropriate work or professional experience, at an additional level.
Outcomes
A graduate of a Postgraduate Diploma is able to:
- show evidence of advanced knowledge about a specialist field of enquiry or professional practice
- engage in rigorous intellectual analysis, criticism and problem-solving.
Credit requirements
The Postgraduate Diploma requires a minimum of 120 credits from levels 7 and above, with a minimum of 72 credits from level 8.
Relationship with other qualifications
A person who holds a Postgraduate Diploma may be eligible to enrol in a Master’s Degree.
Master’s Degree
A Master’s Degree qualifies individuals who apply an advanced body of knowledge in a range of contexts for research, a pathway for further learning, professional practice and/or scholarship. Master’s Degrees usually build on a Bachelor’s Degree, Graduate Diploma, Bachelor Honours Degree or a Postgraduate Diploma. They may also build on extensive professional experience of an appropriate kind. Their outcomes are demonstrably in advance of undergraduate study, and require individuals to engage in research and/or advanced scholarship. Master’s Degrees are constituted in one discipline or coherent programme of study. They may be undertaken by taught courses or research, or by a combination of both.
Credit requirements
The Master’s Degree is at least 240 credits except where:
- it builds on a Bachelor’s Degree with Honours or an equivalent qualification, or significant relevant professional experience, in which cases it can be fewer than 240 but no fewer than 120 credits
- it builds on a three-year Bachelor’s Degree or an equivalent qualification, in which cases it can be fewer than 240 but no fewer than 180 credits. The Master’s Degree must comprise a minimum of 40 credits at level 9 with the remainder at level 8.
Entry
Providers of programmes leading to Master’s qualifications are responsible for establishing entry requirements. The minimum entry qualification for a Master’s Degree is a Bachelor’s Degree or equivalent (to a Bachelor’s Degree listed at level 7 on the NZQF). A programme of study leading to the Master’s Degree is open to those who have met the entrance requirements, including specified levels of attainment, in the programme admission regulations. The minimum entry qualification for a Master’s Degree of fewer than 240 credits but no fewer than 120 credits is either a Bachelor Honours Degree or a Postgraduate Diploma or an undergraduate degree followed by relevant professional experience. Admission as an individual to a Master’s Degree is based on the evaluation of documentary evidence (including the academic record) of the individual applicant’s ability to undertake postgraduate study in a specialist field of enquiry or professional practice.
Structure
Master’s Degrees are structured in three principal ways:
- Entry to a Master’s Degree by thesis is normally based on a Bachelor Honours Degree or a Postgraduate Diploma in the same field of study. The degree includes 120 credits, of which at least 90 credits (at level 9) consist of a research project presented in the form of a thesis, dissertation, substantial research paper or scholarly creative work.
- Entry to a Master’s Degree by coursework and thesis is normally based on an undergraduate degree in the same field of study. The degree includes 240 credits, of which at least 90 credits at level 9 are in the form of a thesis, dissertation, substantial research paper or scholarly creative work, and of which up to 150 credits are from coursework.
- Entry to a Master’s Degree by coursework is normally based on an undergraduate degree achieved at a specified level of attainment. The degree is at least 120 to 240 credits and is achieved through coursework consisting of courses, project work and research in varying combinations. It may build on undergraduate study in the same academic field, or it may build on the more generic graduate attributes of an undergraduate degree in other fields, or in some cases on relevant professional experience. Master’s Degrees that build on generic attributes and/or experience (often called ‘conversion Master’s’) are usually in professional fields and are recognised as appropriate professional preparation by the profession or industry concerned.
Outcomes
A graduate of a Master’s Degree is able to:
- show evidence of advanced knowledge about a specialist field of enquiry or professional practice
- demonstrate mastery of sophisticated theoretical subject matter
- evaluate critically the findings and discussions in the literature
- eesearch, analyse and argue from evidence • work independently and apply knowledge to new situations
- engage in rigorous intellectual analysis, criticism and problem-solving.
If a Master’s Degree includes a component of supervised research of not fewer than 90 credits at level 9, the graduate is also able to:
- demonstrate a high order of skill in the planning, execution and completion of a piece of original research or creative scholarly work
- apply such skills learned during the study programme to new situations. The research should be completed to internationally recognised standards and demonstrate that the graduate has a capacity for independent thinking.
Relationship with other qualifications
A person who holds a Master’s Degree achieved to an appropriate standard, that includes a research component, may be considered for admission to a programme of advanced study and/or original research leading to a Doctoral Degree.
Doctoral Degree
A Doctoral Degree is a research degree whereby the individual becomes an increasingly independent scholar who makes a substantial and original contribution to knowledge.
It is normally the culmination of study which begins at the bachelor level and reaches a stage beyond the masters. For the PhD/DPhil and the named doctorate (e.g. DMus), the development takes place under the guidance of recognised experts in the field of study and under circumstances that allow the individual access to appropriate research resources.
The contribution to knowledge is judged by independent experts applying contemporary international standards of the discipline. The hallmark will be the individual’s capacity for substantial independent research or scholarly creative activity as attested by his/her educational institution and/or as demonstrated by submitted work.
The major component of all doctorates is original research. The body of work that leads to the award of a doctorate will be one or more of the following:
- a thesis (the PhD/DPhil)
- creative work in the visual or performing arts (the PhD/DPhil)
- a thesis or equivalent creative work in combination with coursework (the named doctorate)
- a creative work in the visual or performing arts (the named doctorate) with a thesis (the named doctorate)
- published work.
Credit requirements
A Doctoral Degree requires at least 360 credits and is listed at level 10. The following types of Doctoral Degree are recognised.
Doctorate of Philosophy (PhD/DPhil)
A thesis constitutes the entire body of work on which the award of the qualification will be judged. Coursework may also be prescribed for the individual, but this will only contribute to the preparation for research and acceptance into the doctoral programme. Where appropriate, individuals may present a creative work as part of the thesis requirement.
Doctorate in a specified field or discipline – the named doctorate (e.g. EdD or the DMus)
For a doctorate in a specified field, coursework may contribute to the assessed programme of study, but research or the scholarly creative activity and the associated thesis must occupy at least two full-time academic years and contribute not less than two-thirds of the overall credit for the degree.
The coursework, which is to be at a standard in advance of that expected for a masters paper, must be part of a coherent programme with the research work, and should normally cover no more than one full-time academic year. An individual for a named doctorate must gain a passing grade in both the coursework and the thesis or its creative work equivalent.
Higher Doctorate (e.g. the DSc or the DLitt)
Higher Doctorates are awarded for independent work of special excellence, as judged by leading international experts, which is completed before a person makes an application to enrol for the degree. Individuals will normally be expected to have completed at least ten years of independent work and to have published extensively.
Publication will normally be in scholarly books and/or in reputable international journals. Individuals in the visual or performing arts will have made equally outstanding contributions in their creative work.